Can Gallbladder Stones Be Removed Without Surgery?
Introduction
Gallstones are one of the most common digestive health problems worldwide. Millions of people search each year, asking the same question:
The good news: Yes, in some cases, but not always.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore:
What gallstones are
How gallstones are diagnosed
All non-surgical gallbladder stone treatments
When gallstone surgery becomes necessary
Natural & medical ways to manage gallstones safely
This article is written in clear, patient-friendly language for maximum understanding and search ranking.
What Are Gallstones?
Gallstones are hardened deposits of digestive fluid (bile) that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver.
They can range in size from tiny grains of sand to large stones the size of a golf ball.
Types of Gallstones
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Cholesterol Stones | Most common, made of hardened cholesterol |
| Pigment Stones | Dark stones formed from excess bilirubin |
Many people also confuse gallstones with liver stones, but true liver stones form in bile ducts, not inside the liver tissue itself.
Gallstones Diagnosis: How Doctors Detect Them
Proper gallstone diagnosis is essential before deciding on treatment.
Common Diagnostic Tests
Ultrasound – Most accurate and first-line test
CT Scan – Used when complications are suspected
Blood Tests – Detect infection, liver blockage, or inflammation
HIDA Scan – Checks gallbladder function
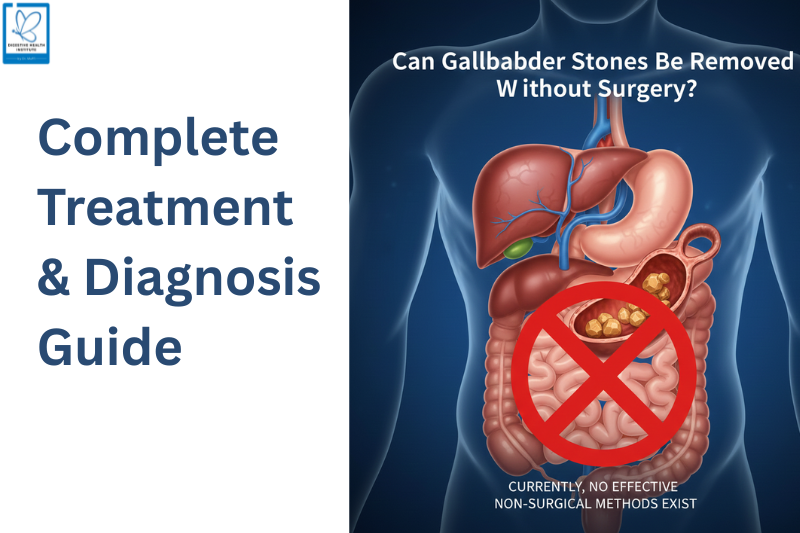
Can Gallbladder Stones Be Removed Without Surgery?
Yes, In Selected Cases
Gallbladder stones can be treated without surgery if:
Stones are small
The gallbladder is still functioning normally.
Symptoms are mild or absent.
Stones are made of cholesterol

Non-Surgical Gallbladder Stones Treatment Options
1. Oral Dissolution Therapy (Medication)
Doctors may prescribe medications such as:
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA)
Chenodeoxycholic acid
These medicines slowly dissolve cholesterol stones over 6–24 months.
Best for: Small, cholesterol-based stones
Limitations: Stones may return once the medication stops
2. Shock Wave Therapy (ESWL)
High-energy sound waves break stones into smaller pieces, which then pass naturally.
Rarely used today, but still an option for select patients.
3. Natural Management (Supportive Care)
These methods do not remove stones, but may prevent worsening:
Low-fat, high-fibre diet
Weight management
Avoid rapid weight loss.
Hydration
Regular meals to promote bile flow
When Is Gallstone Surgery Required?
Despite non-surgical options, gallstone surgery remains the most effective and permanent solution.
Surgery Is Necessary If:
Recurrent pain attacks occur.
Stones block the bile ducts.
Inflammation or infection develops.
Pancreatitis occurs
The gallbladder stops functioning
Most Common Surgery: Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Minimally invasive
Small incisions
Fast recovery
Permanent cure
What Happens If Gallstones Are Left Untreated?
Ignoring gallstones can cause:
Severe abdominal pain
Infection (cholecystitis)
Jaundice
Pancreatitis
Life-threatening complications
Gallbladder Stones Treatment: Which Is Best for You?
| Condition | Best Treatment |
|---|---|
| Small, mild stones | Medication |
| Symptomatic stones | Surgery |
| Recurrent attacks | Surgery |
| Blocked bile duct | Emergency intervention |
| High surgical risk | Medication & monitoring |
A doctor’s evaluation is essential for personalised treatment.