Difference Between Reconstructive and Cosmetic Surgery

Many people assume reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery are the same. While both involve surgical correction and appearance improvement, their purpose, medical need, and insurance coverage are very different.
Understanding the difference between reconstructive and cosmetic surgery helps patients make informed decisions.
What Is Reconstructive Surgery?
Reconstructive surgery is performed to restore normal function and structure of the body after injury, disease, birth defects, or medical conditions.
Common reasons for reconstructive surgery:
- Trauma or accident injuries
- Cancer removal (breast
reconstruction after mastectomy) - Burns and scars
- Congenital defects (cleft lip, club foot)
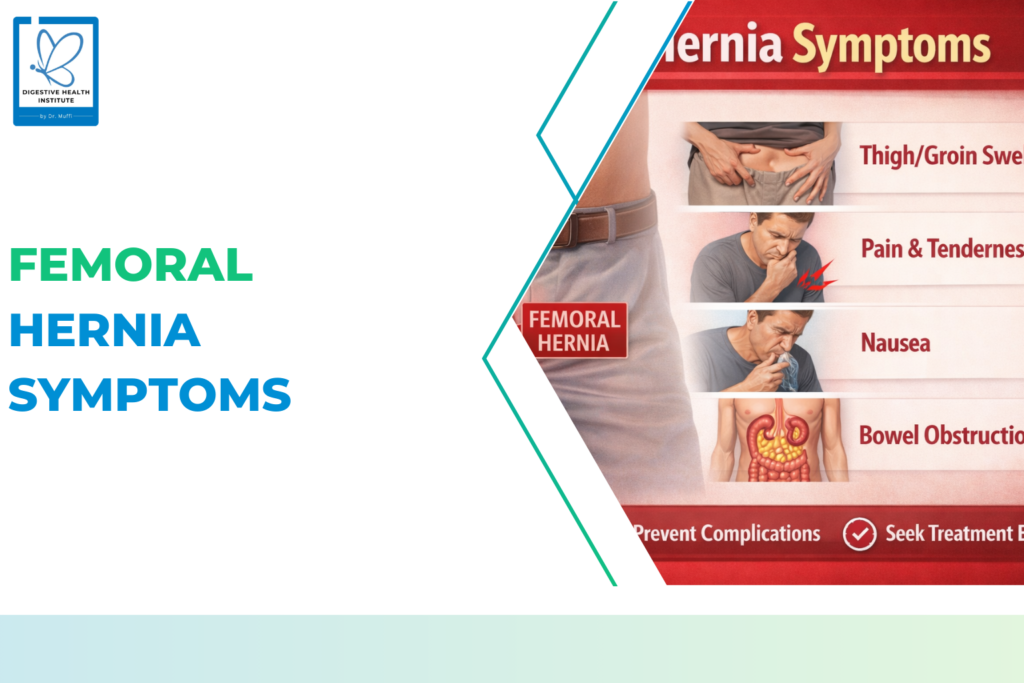
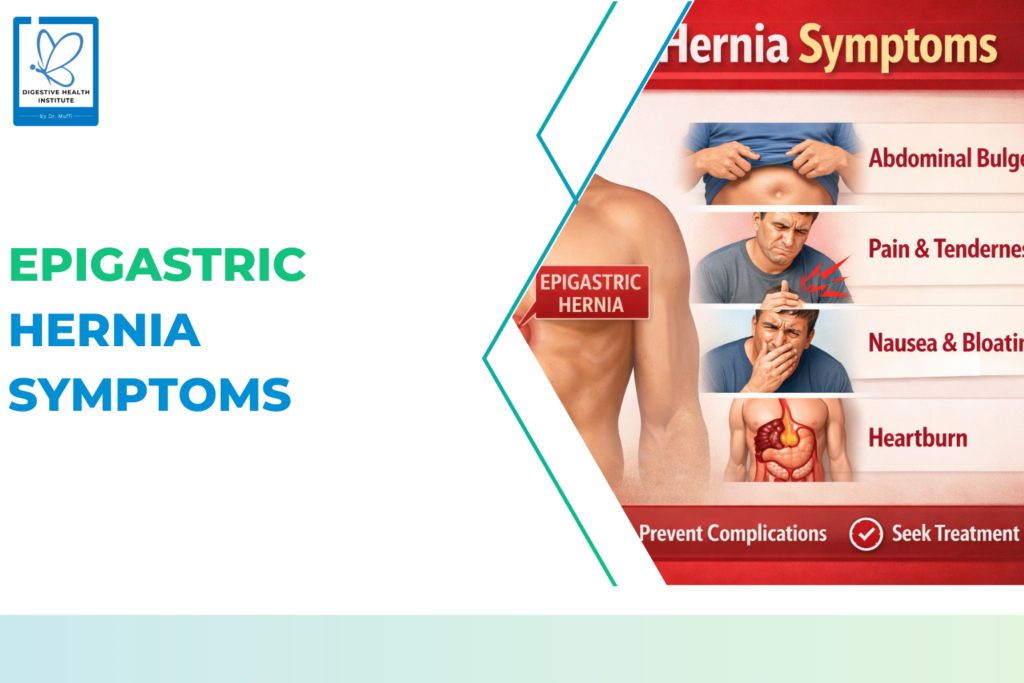
- Hernia repair
- Post-infection tissue damage
->Reconstructive surgery is medically necessary.
What Is Cosmetic Surgery?
Cosmetic surgery is performed to enhance physical appearance in individuals who are otherwise healthy.
Common cosmetic procedures:
- Rhinoplasty (nose reshaping)
- Liposuction
- Tummy tuck (abdominoplasty)
- Facelift
- Botox and fillers
-> Cosmetic surgery is elective, not medically required.
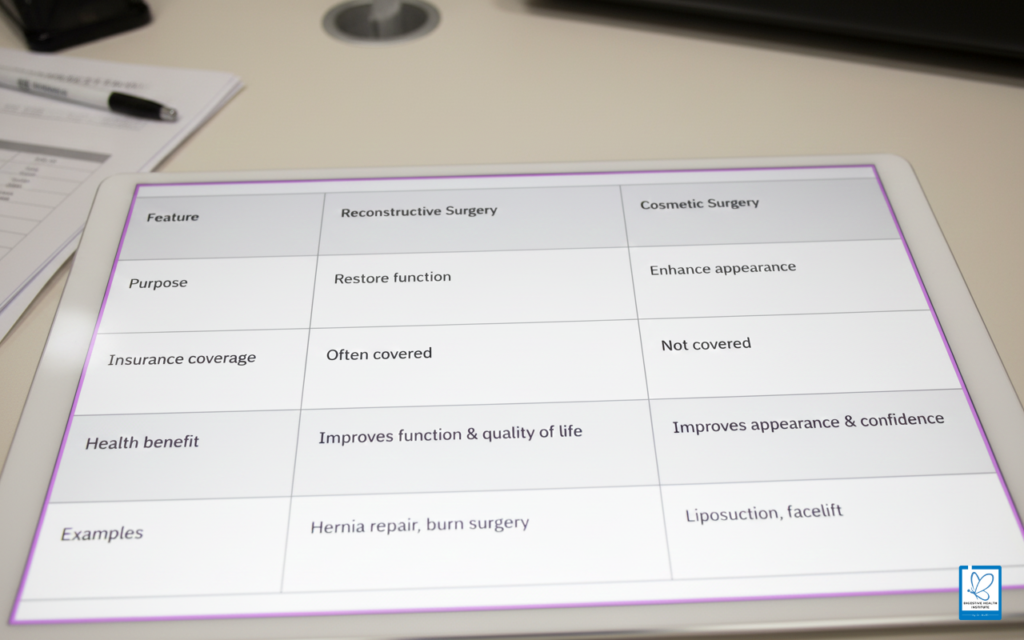
Key Difference Between Reconstructive and Cosmetic Surgery
Feature | Reconstructive Surgery | Cosmetic Surgery |
Purpose | Restore function | Enhance appearance |
Medical necessity | Yes | No |
Insurance coverage | Often covered | Not covered |
Health benefit | Improves function & quality of life | Improves appearance & confidence |
Examples | Hernia repair, burn surgery | Liposuction, facelift |
Can a Surgery Be Both Reconstructive and Cosmetic?
Yes. Some procedures fall into both categories, depending on the situation.
Examples:
- Breast surgery after cancer (reconstructive)
- Nose surgery after trauma (reconstructive)
- Scar revision affecting movement (reconstructive)
If done only for appearance, the same procedure becomes cosmetic.
Which Surgery Is Right for You?
You may need reconstructive surgery if:
- You have pain, functional issues, or medical damage
- Your condition affects daily life
You may consider cosmetic surgery if:
- You want aesthetic improvement
- You are medically healthy
- You have realistic expectations
A qualified surgeon can help decide the right approach.
Are the Risks Different?
Both surgeries carry similar risks:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Scarring
- Anesthesia risks
However, reconstructive surgery often involves complex medical conditions, while cosmetic surgery focuses more on precision and aesthetics.
Recovery Time Comparison
- Reconstructive surgery: Longer recovery depending on medical condition
- Cosmetic surgery: Shorter recovery in most cases
Recovery depends on procedure type and individual health.
Final Thoughts: Reconstructive vs Cosmetic Surgery
The main difference between reconstructive and cosmetic surgery lies in medical necessity. Reconstructive surgery restores function and health, while cosmetic surgery enhances appearance.
Both require expert surgeons, proper counseling, and realistic expectations.
FAQs Difference Between Reconstructive and Cosmetic Surgery
- Is reconstructive surgery the same as cosmetic surgery?
No. Reconstructive surgery is medically necessary to restore function, while cosmetic surgery is elective and focused on appearance enhancement. - Is cosmetic surgery covered by insurance?
Cosmetic surgery is usually not covered by insurance, while reconstructive surgery is often covered when medically required. - Can cosmetic surgery become reconstructive surgery?
Yes. If a cosmetic procedure is performed to correct medical issues or restore function, it may be considered reconstructive. - Who needs reconstructive surgery?
People who have lost normal body function or appearance due to injury, birth defects, cancer surgery, burns, infections, or medical conditions may need reconstructive surgery to restore function and improve quality of life. - What are the two types of reconstruction?
The two main types of reconstruction are tissue reconstruction (using the patient’s own tissue) and implant-based reconstruction (using medical implants to restore shape and structure).
- What is an example of a reconstructive surgery?
An example of reconstructive surgery is breast reconstruction after mastectomy, which restores breast shape following cancer removal. Other examples include cleft lip repair and burn scar correction.