What Causes Hernia in Women?
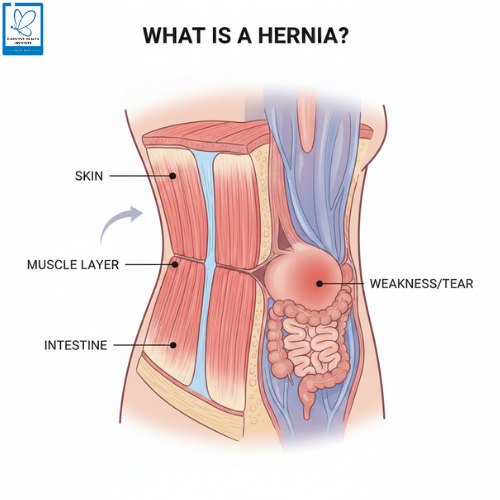
Understanding what causes hernia in women is important because these conditions are often missed or misdiagnosed. A hernia develops when internal tissue pushes through a weakened area of muscle or connective tissue. In women, hernias may present with subtle or deep-seated symptoms that are commonly mistaken for pelvic pain or gynecological issues. Recognizing the underlying causes early can help in timely diagnosis, effective treatment, and safer long-term management.
Understanding Hernias in Women
Unlike men, women may not always develop a visible bulge. Hernias in females frequently cause pressure, heaviness, or aching pain, especially during physical activity or prolonged standing. This makes clinical awareness especially important.
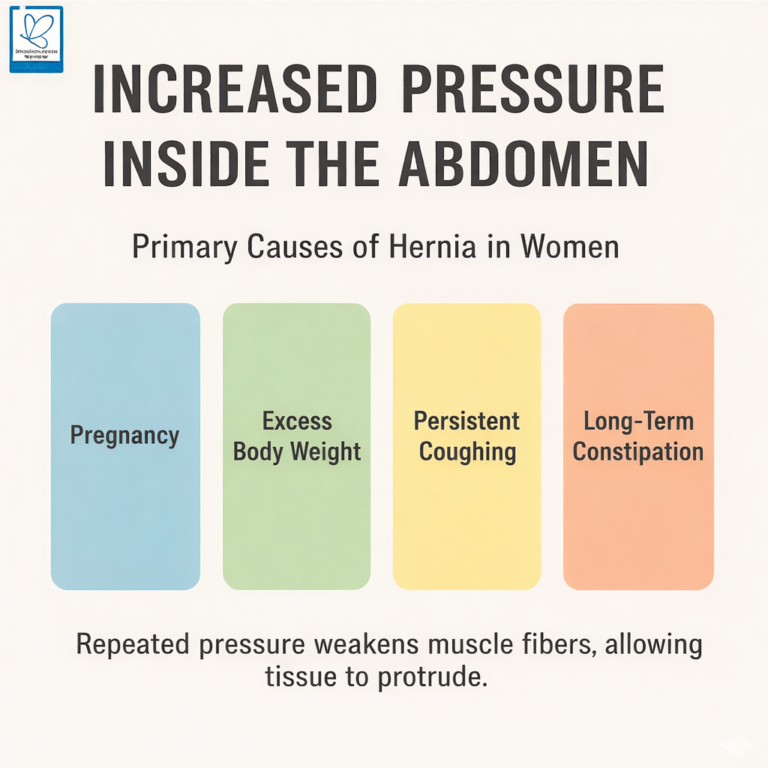
Primary Causes of Hernia in Women
Increased Pressure Inside the Abdomen
Any condition that raises abdominal pressure over time can contribute to hernia formation. This includes:
- Pregnancy
- Excess body weight
- Persistent coughing
- Long-term constipation
Repeated pressure weakens muscle fibers, allowing tissue to protrude.
Muscle and Connective Tissue Weakness
Some women have naturally weaker connective tissue. Hormonal changes, aging, and reduced collagen strength can further weaken the abdominal wall, increasing hernia risk even without heavy exertion.
Pregnancy and Post-Delivery Changes
During pregnancy, abdominal muscles stretch significantly. After childbirth, especially following multiple pregnancies or cesarean sections, muscles may not regain full strength, creating weak points.
Previous Abdominal or Pelvic Surgery
Surgical incisions can disrupt muscle integrity. Over time, scar tissue may weaken, leading to hernia development near the surgical site.
Physical Strain and Improper Movement
Sudden exertion, poor lifting techniques, or returning to intense exercise too quickly after pregnancy or surgery can strain abdominal muscles and contribute to hernia formation.
Risk Factors More Common in Women
- Multiple pregnancies
- Cesarean deliveries
- Pelvic or uterine surgeries
- Obesity or rapid weight changes
- Menopause-related muscle changes
Family history of hernia
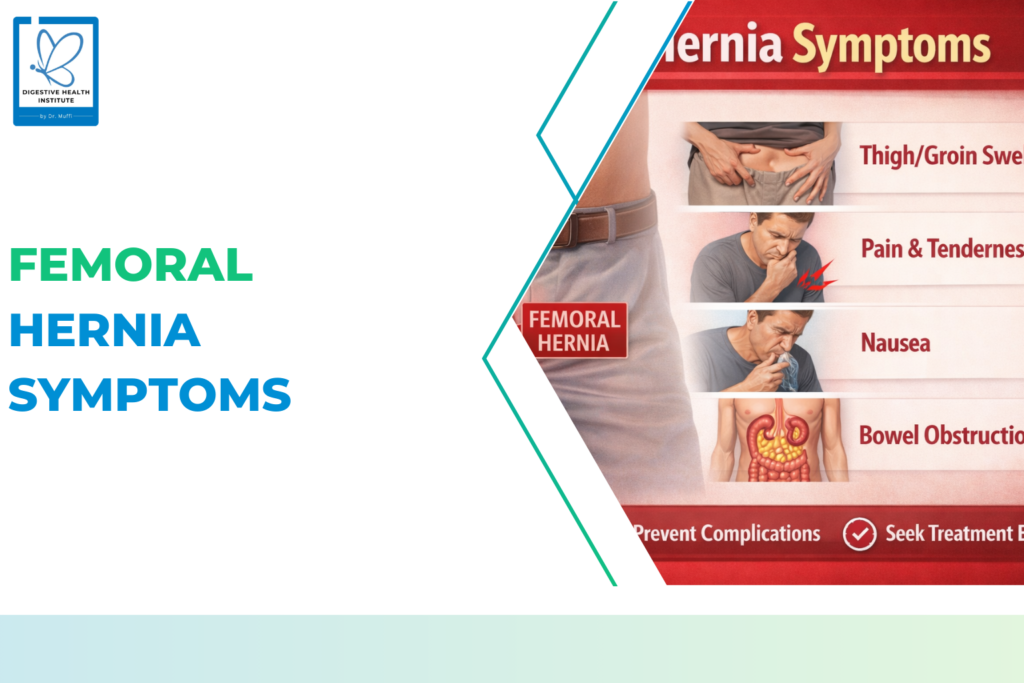
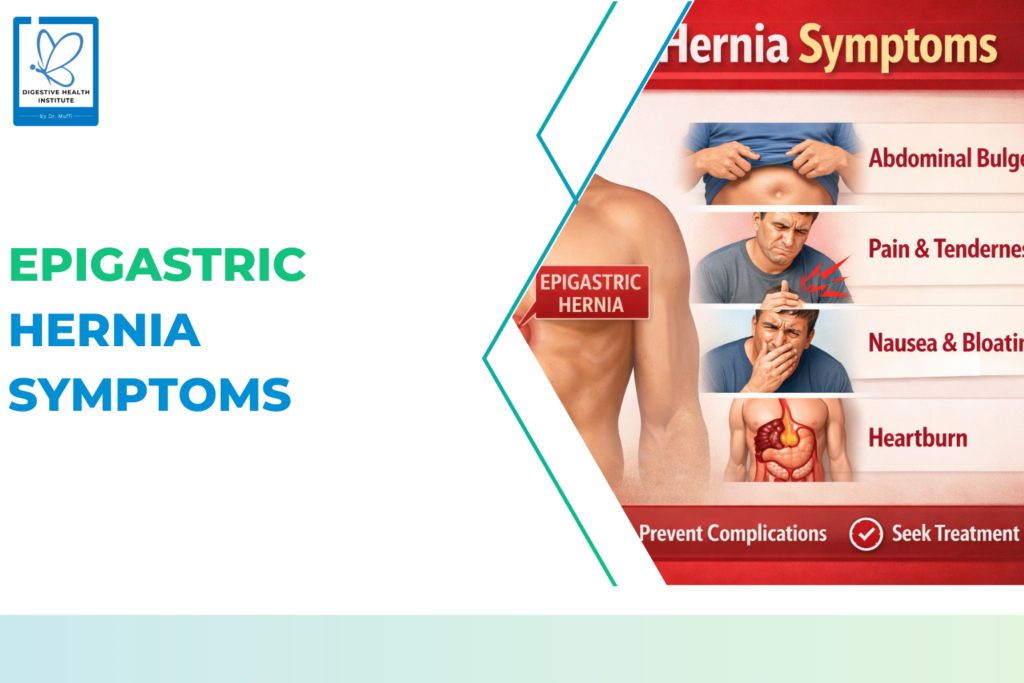
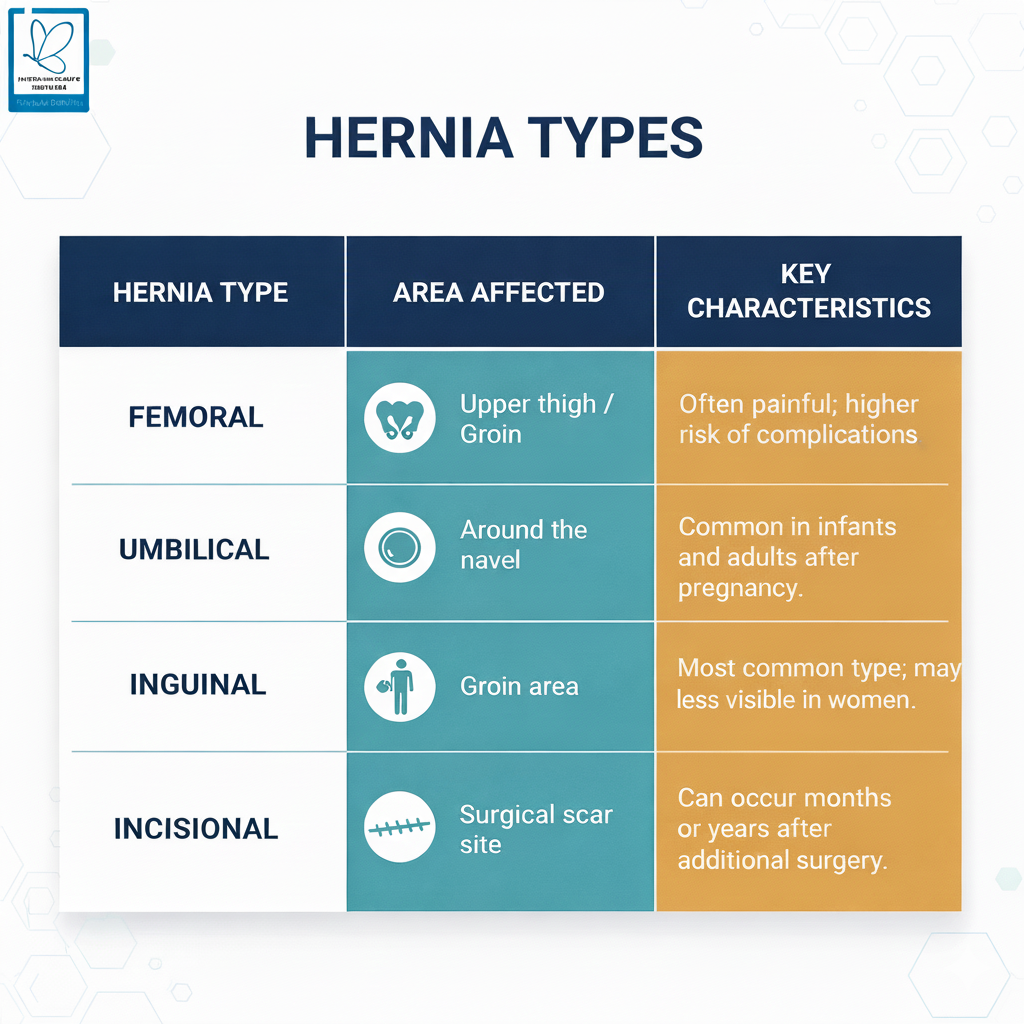
Types of Hernias Seen in Women
Symptoms Women Should Not Ignore
Hernia symptoms can vary, but commonly include:
- Persistent groin or abdominal pain
- Heaviness or pressure sensation
- Pain during lifting or coughing
- Swelling that reduces when lying down
- Unexplained pelvic discomfort
Some women experience pain without swelling, which delays diagnosis.
How Hernias Are Identified
Diagnosis is based on:
- Clinical examination
- Ultrasound imaging
- CT or MRI scans for complex or hidden hernias
Accurate diagnosis is essential to avoid serious complications.
Treatment Approach
Conservative Measures
Lifestyle changes may reduce discomfort but do not correct the hernia. These include:
- Avoiding strain
- Managing constipation
- Activity modification
Surgical Repair
Surgery is the only definitive treatment. The method depends on hernia type, size, and patient factors. Modern techniques allow precise repair with faster recovery.
Recovery Expectations
Most women resume light activities within days. Full recovery depends on:
- Type of repair
- Overall health
- Adherence to post-operative guidance
Can Hernias Be Prevented?
Risk can be reduced by:
- Maintaining healthy weight
- Strengthening core muscles safely
- Using correct lifting techniques
- Allowing proper recovery after childbirth or surgery
- Treating chronic cough or constipation early
When Medical Advice Is Needed
Seek evaluation if:
- Pain increases over time
- A new swelling appears
- Daily activities become uncomfortable
- Symptoms worsen suddenly
Prompt care lowers the risk of complications.
Key Takeaway
Hernias in women develop due to a combination of muscle weakness, physical strain, hormonal changes, and increased abdominal pressure. Understanding what causes hernia in women is essential because symptoms are often subtle and easily overlooked. Early awareness and timely medical evaluation play a crucial role in safe diagnosis and effective management.
FAQs About the What Causes Hernia in Women
Q1.What are the symptoms of a hernia in a woman?
Symptoms of a hernia in a woman may include a dull or sharp pain in the abdomen or groin, a feeling of pressure or heaviness, discomfort while standing, lifting, or coughing, and swelling that may reduce when lying down. Some women experience pain without a visible bulge, especially with femoral or inguinal hernias.
Q2. Is a hernia in a woman serious?
A hernia can become serious if left untreated. While some hernias remain stable for a time, others can lead to complications such as trapped tissue or reduced blood supply, which may require urgent medical care. Early evaluation helps prevent these risks.
Q3. How do they fix a hernia on a female?
Hernias are usually repaired through surgery, where the weakened muscle area is strengthened and the protruding tissue is placed back in position. The repair can be done using open or minimally invasive techniques, depending on the type and size of the hernia.
Q4. Can you fix a hernia without surgery?
No. A hernia cannot be permanently fixed without surgery. Lifestyle changes may reduce discomfort, but they do not repair the muscle weakness causing the hernia.
Q5. What are the early warning signs of a hernia?
Early warning signs include mild discomfort in the abdomen or groin, pain that worsens with activity or coughing, a feeling of heaviness, or a small swelling that appears and disappears. In women, early signs may be subtle and are sometimes mistaken for pelvic or digestive issues.